Africa is not only rich in cultural heritage and breathtaking landscapes but also offers incredible investment opportunities.
But investing in the continent requires patience as strategies that succeed in one country may not work in others.
In this post, we explore five compelling reasons why you should consider investing in Africa, even if you reside outside the continent.
A young and fast-growing market
Africa has over 1.3 billion people and is the world’s youngest region, with almost 60% of its population under 25 years old while the median age is 19.
The continent also boasts a rapidly growing population and an expanding middle class. According to the World Economic Forum, by 2030, over 40% of Africans will belong to the middle or upper classes, and there will be a higher demand for goods and services.
By that time, household consumption is expected to reach $2.5 trillion, more than double that of 2015 at $1.1 trillion.
With increasing urbanization and rising disposable incomes, it presents an untapped market ready for investors to tap into a vast consumer base, which offers tremendous growth potential across various sectors.
Innovation and entrepreneurship
Africa is witnessing a remarkable surge in innovation and entrepreneurship. From fintech startups to renewable energy solutions, African entrepreneurs are harnessing technology to solve local challenges and create scalable businesses.
The continent has produced at least seven unicorns—private companies worth $1 billion or more.
One such startup is Flutterwave, a Nigerian fintech unicorn revolutionizing digital payments across the continent. Another standout is Andela, a pan-African company connecting skilled software developers with global companies.
These innovative startups demonstrate Africa’s increasing prominence in the global tech landscape, fueling economic growth and driving technological advancements across the continent.
By investing in African startups and venture capital funds, you can support these innovative minds while potentially benefiting from their future successes.
Rapid digital transformation
Africa has witnessed a rapid digital transformation in recent years, revolutionizing various sectors.
With increasing internet penetration, mobile connectivity, and innovative solutions, the continent has embraced technology in all facets of life.
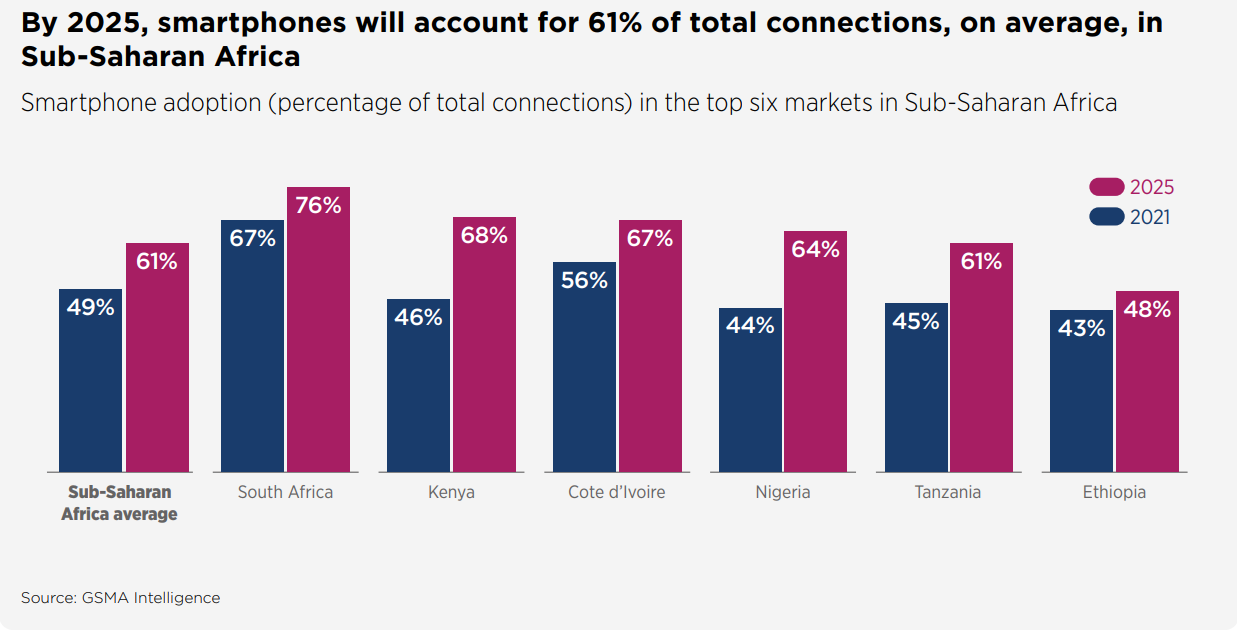
According to GSMA, Africa will add nearly 100 million new subscribers by 2025, bringing the total number of subscribers to 613 million – almost half of the region’s population.
More so, the contribution of the mobile industry to its GDP will grow to almost $155 billion.
From mobile banking to e-commerce platforms, Africa’s digital revolution is empowering individuals, bridging the digital divide, and creating opportunities for socio-economic development across the continent.
The abundance of natural resources
Africa is blessed with an abundance of natural resources that contribute significantly to its economic potential.
With vast mineral deposits, the continent holds a substantial share of the world’s reserves of gold, diamonds, platinum, and other precious metals. It is also rich in oil and gas resources, with countries like Nigeria, Angola, and Algeria being major producers.
Additionally, Africa possesses extensive reserves of timber, fertile agricultural land, and a diverse range of flora and fauna.
These resources present immense opportunities for economic growth, industrial development, and foreign investment.
With the right investment strategy, you can benefit from the continent’s rich resources and contribute to its sustainable development.
Stronger and more dynamic economies
Africa is experiencing a remarkable shift towards diverse and stronger economies. With a focus on innovation, entrepreneurship, and sustainable development, several African nations are making significant strides.
The continent has witnessed a surge in technological advancements, fostering digital transformation and leapfrogging traditional infrastructure barriers.
Countries like Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa have emerged as tech hubs, attracting global investments and nurturing homegrown startups. African governments are also supporting sectors like agriculture, renewable energy, and manufacturing to stimulate economic growth and reduce dependency on commodities.
Regional collaborations, such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), are promoting intra-African trade, opening up new markets, and encouraging economic integration.
Africa’s total exports are projected to reach approximately $952 billion by 2035, driven by the growth of regional trade and enhanced connectivity, according to a new report by Standard Chartered.
This momentum towards diverse and stronger economies is poised to unleash Africa’s immense potential, empowering its people and offering investors exciting opportunities across the continent.
Investing in Africa presents a world of opportunities for those outside the continent.
With an untapped market, abundant resources, growing infrastructure, a vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem, and favorable policies, Africa is poised for economic growth and development.
Disclaimer: This material has been presented for informational and educational purposes only. The views expressed in the articles above are generalized and may not be appropriate for all investors. The information contained in this article should not be construed as, and may not be used in connection with, an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy or hold, an interest in any security or investment product. There is no guarantee that past performance will recur or result in a positive outcome. Carefully consider your financial situation, including investment objective, time horizon, risk tolerance, and fees prior to making any investment decisions. No level of diversification or asset allocation can ensure profits or guarantee against losses. Articles do not reflect the views of DABA ADVISORS LLC and do not provide investment advice to Daba’s clients.