There are not many places to look but up in the new year for African tech stakeholders after what turned out to be a tough 2023 for startups globally.
This year, budgets and valuations were cut, business models revised, layoffs were frequent, and some startups shuttered as the harsh realities of a funding downturn, mismanagement, and fraud took their toll on African tech.
It’s time to take stock of the last 12 months in what’s been a rollercoaster year. Read on to discover the major themes in Africa’s tech ecosystem.
The venture funding market shrinks
The exuberance of 2022’s VC landscape gave way to a stark reality in 2023, with funding plummeting by around half globally in the first half of the year.
This dramatic shift coincided with hikes in interest rates, which had a chilling effect on fundraising. For every 1% hike in interest rates, there was an alarming 3.2% decline in VC capital.
This tightening environment not only reduced the pool of VC money available to startups but also made debt financing, a potential alternative, a less viable option due to higher borrowing costs.
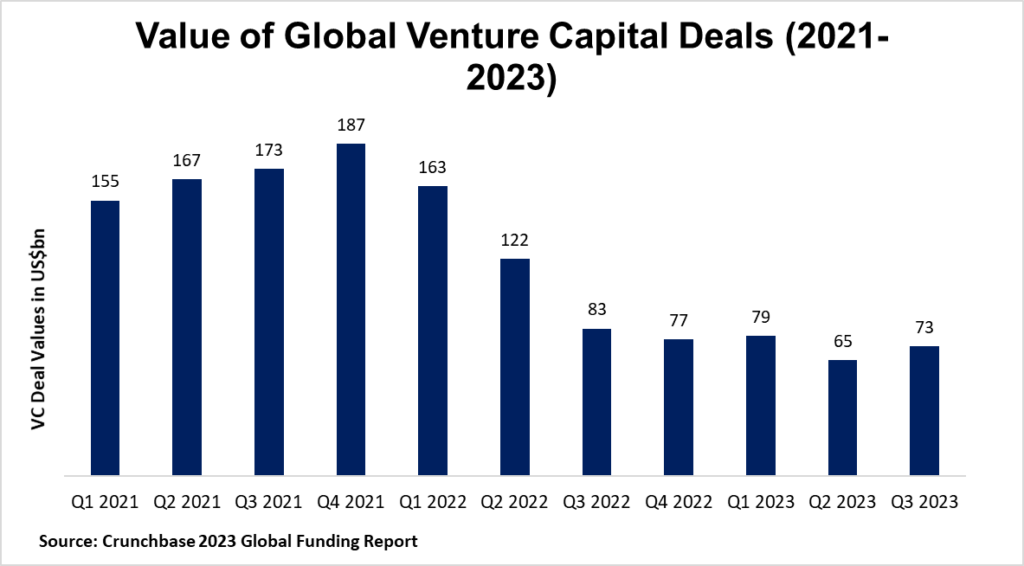
After a bullish 2022 in which Africa was the only continent to record growth in venture funding values, there was no escaping the downturn this year.
The funding winter reached the continent in the H1 2023. Startup funding plunged to just over $1bn, a stark drop from $3.5bn the year before, per AVCA data.
Investors completed 263 deals – a 40% reduction in both deal volume and funding compared to the previous year.
Although African startups staged an impressive comeback in Q3 2023, with funding jumping by 28% compared to the year before.
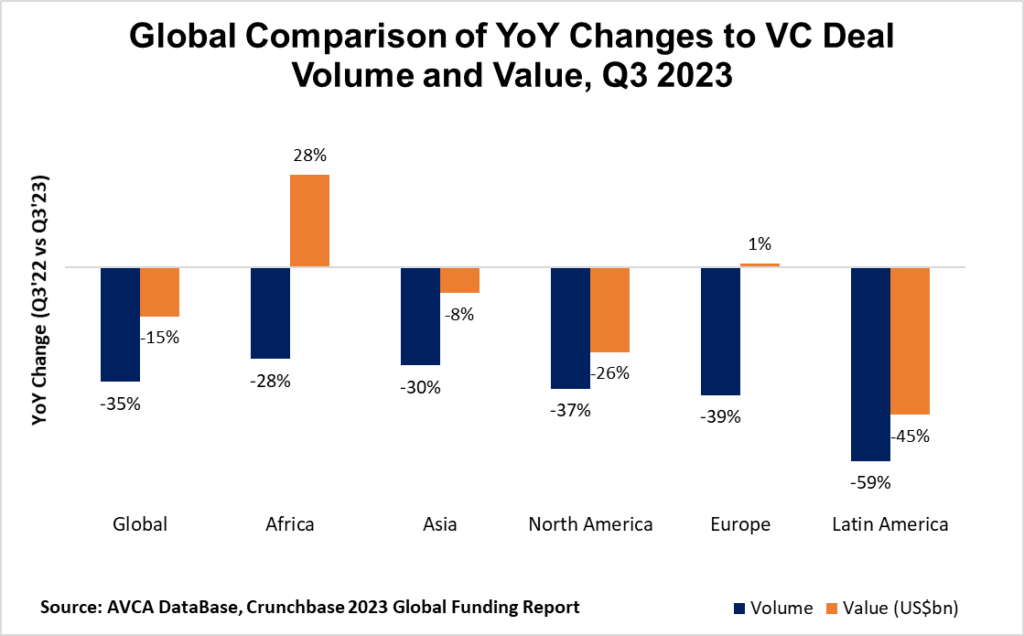
The general slowdown prompted a reshuffle, with investor focus shifting towards nurturing young startups in their early stages or mature players nearing unicorn status.
Most likely Africa’s VC funding figures fell far from 2022 levels. The final tally as of Q3 2023 to date, per AVCA, stood at $2.95bn – down from the $4.3bn that was raised by the same point last year.
That means Africa’s venture capital industry managed to attract two-thirds (69%) of the capital it accrued by September 2022, and a more disappointing 56% of the total funding last year.
While VC funding is harder to come by, Development Finance Institutions (DFIs)—such as the IFC, BII, US DFC, and Proparco—are becoming more active in the tech startup landscape.
Venture debt & hybrid rounds become more frequent
2023’s funding scorecards are yet to roll out but available estimates suggest the continent’s startups still managed to attract more than $5bn.
Compared to previous years, a higher portion of the total funding is likely to be in the form of venture debt, which has become an alternative source of capital for African startups.
Notable in startup fundraising announcements this year is the growing frequency of mixed equity and debt funding rounds.

Examples include:
- Okra Solar’s Series A round ($7.85m equity and $4.15m debt);
- Complete Farmer’s pre-Series A funding round ($7m equity and $3.4m debt)
- Wetility’s $50m fundraising included a $33m commercial debt package from a consortium of commercial and development banks
While venture debt shines as a catalyst for early-stage ventures, providing crucial working capital to fuel their growth, it’s also increasingly powering expansion for more established startups.
This is the case with:
- Mobility FinTech startup Moove Africa. It has raised $325m to date ($150m in equity and over $175m in debt)
- Kenyan solar home system provider d.Light’s $125m securitization facility. The company’s total securitized financing is $490m since 2020
An uptick in startup shutdowns, pivots & downsizing
With global macro headwinds seeing investors cut fewer checks and some reportedly renege on commitments, a slew of startups were forced to downsize, pivot, or in many cases, close up shop.
At least 15 African startups shuttered this year, including those with once highly-celebrated status on the continent: 54 Gene, Dash, Sendy, WhereIsMyTransport, Lazerpay, Zumi, Zazuu, Hytch, Okada Books, Pivo, Vibra, Redbird, Bundle Africa, Spire, Qefira.
Combined, these startups raised over $200m in disclosed VC funding while operational.
Meanwhile, others like Copia, MarketForce, and Twiga Foods have had to change the way they operate.
It’s noteworthy that the funding slowdown has hit a certain type of African startups hardest—well-funded ventures chasing growth-at-all-costs strategies.
Cleantech/climate-tech now as popular as fintech
The tide is rising for climate tech (comprising innovations across agriculture, clean energy, sustainable materials, environmental sustainability, e-mobility, and nature-based solutions) in Africa.
Last year, funding to the sector grew 3.5 times to over $860m, making it Africa’s most funded after fintech.
It has maintained the second spot so far this year, per AVCA report. Data from Africa: The Big Deal shows the sector accounts for 32% of total VC funding as of Q3, behind fintech’s 35%.
And over the past 12-18 months, several VC firms—among them Satgana, Catalyst Fund, Equator, and EchoVC—have introduced funds to support startups in the sector.
The timing of this surge in climate funding couldn’t be better as Africa grapples with the increasingly severe impacts of climate change, we write in our Pulse54 newsletter, which explores climate tech in general and active players in the sector.
Spotlight on fraud & founder misconduct
Amidst the remarkable growth of Africa’s tech ecosystem, shadows loom over malpractices that impede the full potential and integrity of the continent’s startup landscape.
In 2023 alone, numerous unsettling reports emerged, depicting common themes such as financial misappropriation, deficient or corporate malfeasance, instances of sexual harassment, and the prevalence of toxic work cultures.
Startups like Ghana’s Dash and Float, Egypt’s Capiter, South Africa’s Springleap, and Nigeria-based companies such as PayDay, 54Gene, and Patricia were implicated.
More recently, Tingo was charged by the US SEC, accused of engaging in a “massive fraud” involving “billions of dollars of fictitious transactions,” all under the leadership of CEO Dozy Mmobuosi.
The lessons drawn from the challenges of 2023 underscore the critical need for regulatory clarity to eliminate grey areas in compliance.
Furthermore, investors must prioritize ensuring proper governance to safeguard the integrity of the African startup ecosystem.
Mergers & acquisitions become a survival strategy
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) have emerged as a primary exit strategy and, in the current depressed funding environment, a lifeline for African startup founders.
In Q1 2023 alone, seven M&A deals took place in the African startup ecosystem worth over $710m. Tunisia-based InstaDeep’s $682m acquisition in January by Germany’s BioNTech accounted for much of that.
By the end of the year’s first half, there had been at least 16 M&A deals per Big Deal data. About half of them reportedly involve struggling startups.
While this year’s total is likely to be some way off 2022’s 44 deals, one fact remains true: M&As have become a prominent feature of the African tech ecosystem.
Limited funds and the fragmented nature of the African tech market are major drivers.
The presence of numerous small and medium-sized companies across various regions and sectors makes consolidation through M&As a strategic move.
This approach creates larger, more diversified startups that can better compete globally and attract investment.
In addition, African startups are currently viewed as less liquid assets compared to other markets, primarily due to limited exit opportunities.
Thus, as the quest for a reliable path to liquidity in the African tech ecosystem grows, M&As become a viable option for venture capitalists and investors to explore.
Other noteworthy moments and highlights of the year
- Starlink, a satellite internet service of Elon Musk-owned SpaceX, became operational in 6 African countries
- Nigeria lifted a ban on cryptocurrency imposed by the Central Bank almost 3 years ago
- Egypt’s MNT-Halan raised $400m in an equity and debt round that saw it become Africa’s latest unicorn (a private company valued at $1bn or more).
- Bosun Tijani, founder of CcHUB, was appointed as Nigeria’s minister of communications, innovation, and digital economy
- Wasoko and MaxAB, Africa’s leading e-retailers from Kenya and Egypt, are exploring a possible deal that could lead to African tech’s largest merger
- Jumia and Bolt shut down their food delivery businesses amid struggles that underscore the challenging nature of the industry
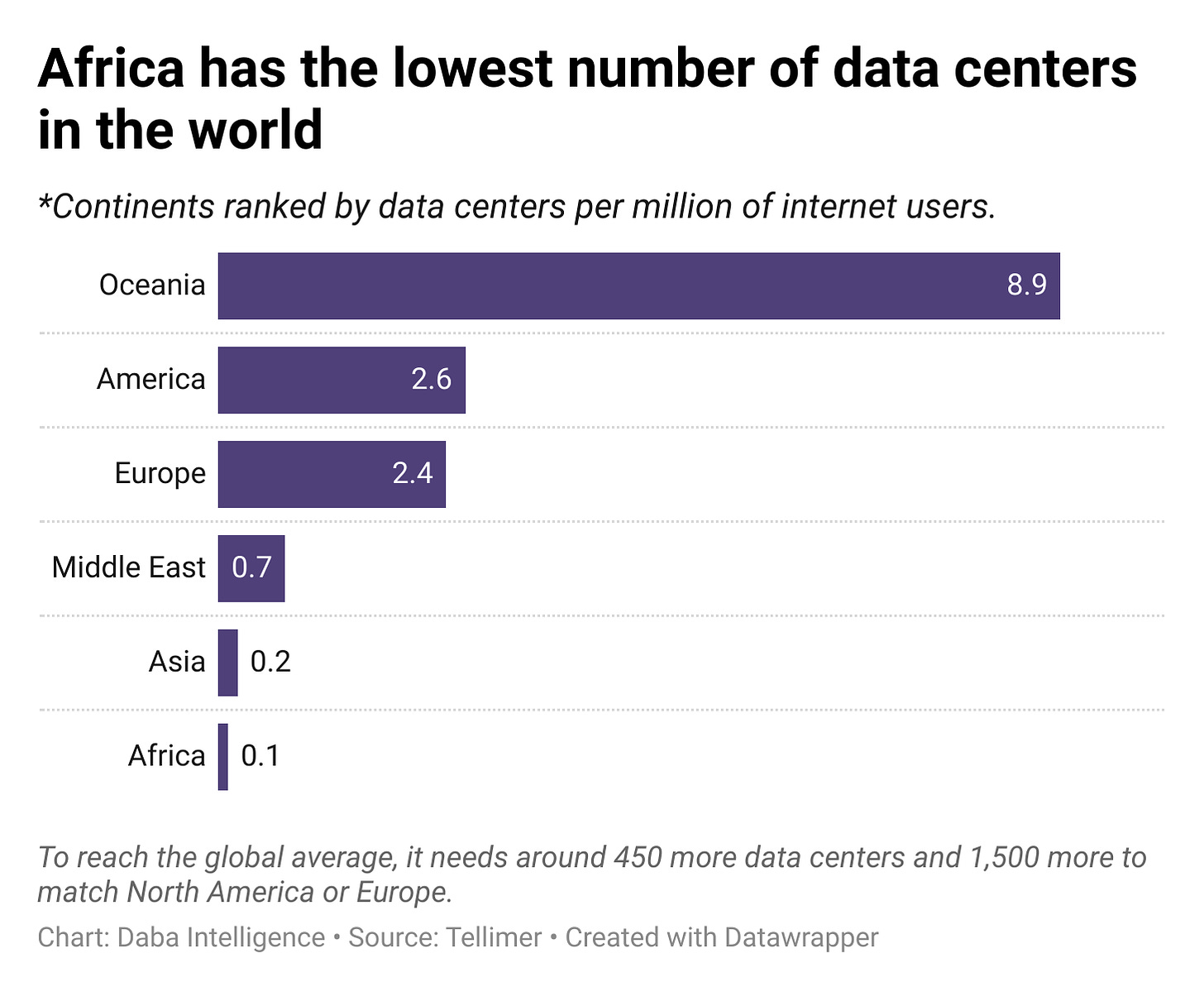
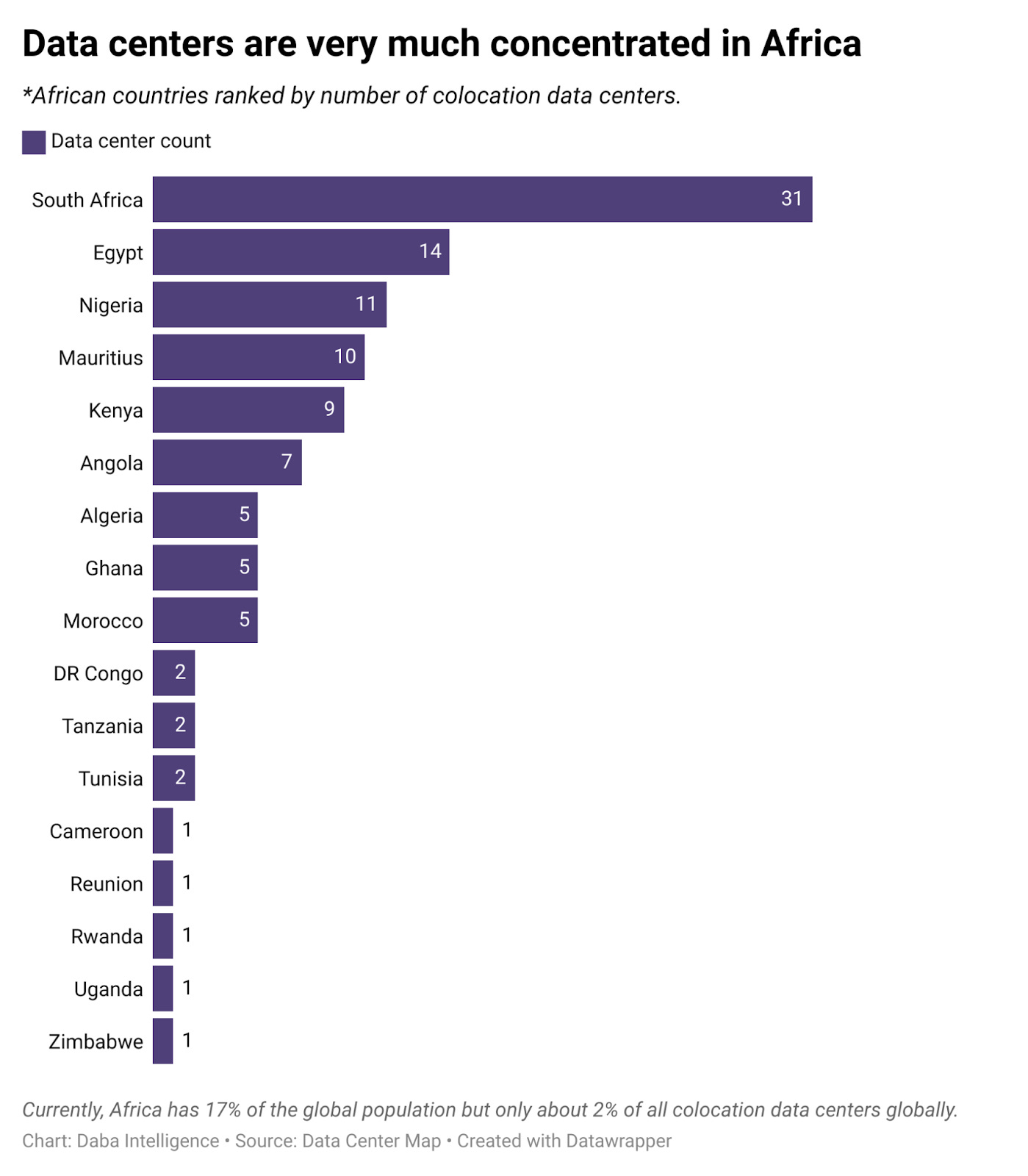
- And digital infrastructure, especially data centers, continues to draw the attention and backing of investors—from telco giants to private equity firms.
Closing Notes
As 2023 hurtles to a close, the question on everyone’s mind is will 2024 be better?
Perceptions of industry performance and expectations for the future vary.
For one, many factors that kept VC activity subdued in the continent this year are still present going into the new year: inflationary pressure, currency volatility, debt worries, muted economic growth, high interest rates, and geopolitical tensions, among others.
But even amidst the uncertainty, investors remain optimistic and Africa’s tech ecosystem is as resilient as ever.
We’re down to the last hours of what’s been a rollercoaster year. Daba wishes you happy holidays and a prosperous new year ahead!