Lorsqu’il s’agit d’ETFs africains, ces fonds suivent généralement des indices représentant un panier d’entreprises africaines ou des secteurs spécifiques de l’économie africaine.
La communauté d’investissement mondiale se tourne de plus en plus vers le continent africain, reconnaissant son immense potentiel de croissance et ses opportunités économiques diversifiées.
En conséquence, un nombre croissant de Fonds Négociés en Bourse (ETFs) inclut désormais des participations significatives en actions africaines, offrant aux investisseurs un moyen pratique d’accéder à ce marché émergent.
Cependant, il est crucial de comprendre que l’Afrique n’est pas une entité homogène. C’est un vaste continent composé de 54 pays, chacun avec son paysage culturel, politique et économique unique. Cette diversité présente à la fois des opportunités et des défis pour les investisseurs cherchant à s’exposer aux marchés africains.
Pour ceux qui cherchent à ajouter des investissements africains à leur portefeuille, les ETFs offrent un excellent point d’entrée. Ce guide complet vous aidera à comprendre ce que sont les ETFs africains, comment ils fonctionnent et comment vous pouvez les utiliser pour atteindre vos objectifs d’investissement.
Lire aussi : Qu’est-ce qu’un Fonds Négocié en Bourse (ETF) ?
Démystifier les ETFs africains : Structure et Fonction
Les fonds négociés en bourse (ETFs) sont des véhicules d’investissement visant à répliquer la performance d’un indice de marché ou d’une commodité spécifique.
En ce qui concerne les ETFs africains, ces fonds suivent généralement des indices représentant un panier d’entreprises africaines ou des secteurs spécifiques de l’économie africaine.
Caractéristiques Clés des ETFs africains
Diversification : Les ETFs africains offrent une exposition à une gamme d’entreprises de différents pays et secteurs, aidant à répartir le risque.
Liquidité : Les ETFs sont négociés sur les bourses, offrant aux investisseurs la possibilité d’acheter et de vendre des actions tout au long de la journée de négociation.
Transparence : La plupart des ETFs divulguent leurs avoirs quotidiennement, permettant aux investisseurs de savoir exactement ce qu’ils possèdent.
Efficacité des coûts : En général, les ETFs ont des ratios de dépenses inférieurs par rapport aux fonds communs de placement gérés activement.
Accessibilité : Les investisseurs peuvent obtenir une exposition aux marchés africains sans les complexités de la propriété directe d’actions sur les marchés étrangers.
Types d’ETFs
ETFs Simples : Ces fonds détiennent directement les actions qui composent l’indice qu’ils suivent. Ils sont souvent plus rentables et simples.
ETFs Complexes : Ceux-ci peuvent utiliser des dérivés ou d’autres stratégies pour atteindre leurs objectifs d’investissement. Bien qu’ils puissent offrir des avantages uniques, ils peuvent comporter des risques et des coûts supplémentaires.
Les investisseurs doivent soigneusement considérer quel type s’aligne le mieux avec leur stratégie d’investissement et leur tolérance au risque.
Le Marché des ETFs en Afrique : Options Disponibles
Le marché des ETFs en Afrique, bien qu’encore en développement, offre une gamme d’options pour les investisseurs. Voici un aperçu de certains acteurs clés dans cet espace :
Titans Continentaux : ETFs Africains Généralisés
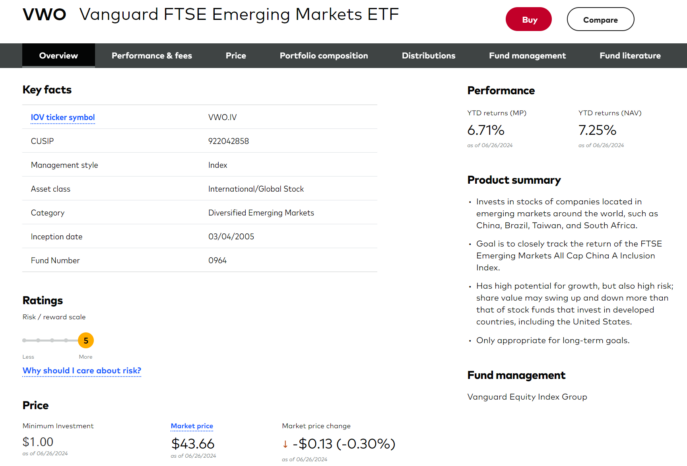
Le Vanguard FTSE Africa Index Fund ETF (KWA)
KWA se distingue comme le plus grand ETF africain par les actifs sous gestion (AUM), avec 2,5 milliards de dollars. Ce fonds offre une exposition à 40 grandes entreprises à travers le continent, y compris des géants comme Standard Bank en Afrique du Sud et First Bank au Nigeria.
Caractéristiques clés de KWA :
- Exposition continentale large
- Focus sur les actions à grande capitalisation
- Ratio de dépenses relativement bas de 0,08 %
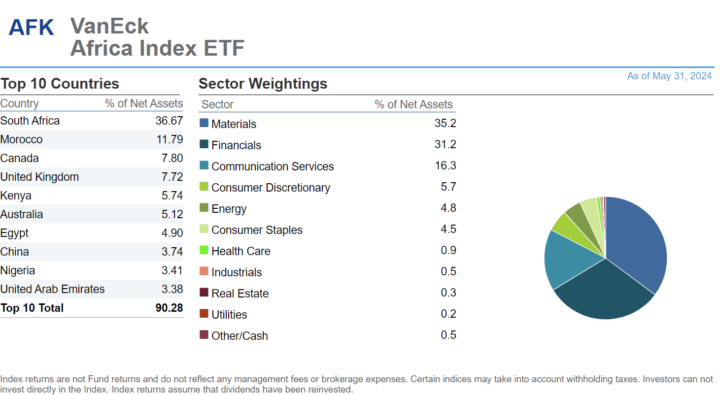
Le VanEck Africa Index ETF (AFK®)
AFK cherche à répliquer, avant frais et dépenses, la performance en prix et rendement de l’indice MVIS® GDP Africa (MVAFKTR), qui comprend des cotations locales d’entreprises incorporées en Afrique et des cotations d’entreprises incorporées hors d’Afrique mais ayant au moins 50 % de leurs revenus/actifs liés en Afrique.
Caractéristiques clés d’AFK :
- Exposition continentale aux plus grandes économies africaines
- Focus sur les actions à grande capitalisation et diversité sectorielle
- Un ratio de dépenses de 1,13 %
Opportunités Spécifiques à un Pays : ETFs Africains Ciblés
Pour les investisseurs cherchant à s’exposer à des économies africaines spécifiques, certains ETFs se concentrent sur des pays individuels :
iShares MSCI South Africa ETF (EZA)
L’iShares MSCI South Africa ETF cherche à suivre les résultats d’investissement d’un indice composé d’actions sud-africaines. Il offre une exposition à de grandes et moyennes entreprises en Afrique du Sud, un accès ciblé au marché boursier sud-africain et est utilisé pour exprimer une vue d’un seul pays.
Jusqu’à sa liquidation récente, BlackRock exploitait l’ETF iShares de 400 millions de dollars au Nigeria et au Kenya.
Ces ETFs spécifiques à un pays permettent aux investisseurs de cibler des économies qu’ils estiment avoir un potentiel de croissance particulier ou de diversifier leur exposition africaine à travers plusieurs fonds axés sur des pays.
ETFs Sectoriels ou de Commodités Africaines
Certains ETFs se concentrent sur des secteurs particuliers de l’économie africaine ou certaines commodités.
Market Vectors Africa Index ETF (AFK)
Cet ETF offre une exposition à des entreprises cotées en bourse dont le siège est en Afrique ou qui génèrent la majorité de leurs revenus en Afrique.
NewGold Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)
Le NewGold Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) permet aux investisseurs d’investir dans un instrument de dette dont la valeur suit le prix de l’or.
Les ETFs sectoriels peuvent être utiles pour les investisseurs ayant des perspectives sur des industries particulières ou souhaitant capitaliser sur des tendances économiques spécifiques en Afrique.
Réduction des Risques : ETFs Africains Couvert en Devises
Investir sur les marchés étrangers implique toujours un risque de change. Lorsque vous investissez dans un ETF africain standard, vous êtes exposé non seulement à la performance des actions sous-jacentes mais aussi aux fluctuations du taux de change entre votre devise nationale et les devises des pays africains représentés dans l’ETF.
Les ETFs couverts en devises visent à atténuer ce risque. Ces fonds utilisent divers instruments financiers pour compenser l’impact des fluctuations de change sur la performance de l’ETF. Par exemple, le Vanguard FTSE Africa Hedged Index Fund ETF (VFA) hypothétique viserait à fournir les rendements des actions africaines tout en minimisant l’impact des mouvements de change.
Principaux avantages des ETFs couverts en devises :
- Réduction de la volatilité due aux fluctuations de change
- Focus plus clair sur la performance des actions sous-jacentes
- Potentiel de rendements plus stables en période de turbulence sur les marchés des devises
Cependant, il est important de noter que la couverture peut également limiter les gains potentiels si les devises africaines s’apprécient par rapport à votre devise nationale.
Indices des ETFs Africains : La Base de la Construction des Fonds
La plupart des ETFs africains sont construits autour de deux indices principaux :
MSCI Emerging and Frontier (EFM) Africa Top 50 Capped Index
- Suit les 50 plus grandes entreprises des marchés émergents et frontières en Afrique
- Limite la pondération des pays et entreprises individuels pour assurer la diversification
- Fournit une exposition équilibrée aux plus grandes économies du continent
- Suit 30 grandes actions cotées en Afrique ou explorant principalement des actifs africains
- Également exposé à trois zones : Afrique du Sud, Afrique du Nord (y compris le Maroc et l’Égypte) et Afrique subsaharienne (hors Afrique du Sud)
- Limite les constituants individuels à 10 % pour éviter la surconcentration
Ces indices offrent différentes approches pour capturer le marché africain, permettant aux investisseurs de choisir l’exposition qui correspond le mieux à leur thèse d’investissement.
Comment Investir dans les ETFs Africains
Les investisseurs ont plusieurs options pour ajouter des ETFs africains à leurs portefeuilles :
Comptes de Courtage Traditionnels : La plupart des courtiers en ligne majeurs offrent un accès à une large gamme d’ETFs, y compris ceux axés sur l’Afrique. Les investisseurs peuvent acheter des actions d’ETFs africains comme ils le feraient pour toute autre action ou ETF.
Robo-Conseillers : Certaines plateformes de robo-conseillers ont commencé à inclure des ETFs africains dans leurs allocations de portefeuille automatisées, notamment pour les investisseurs recherchant une exposition aux marchés émergents.
Plateformes d’Investissement Numériques : L’essor de la fintech en Afrique a conduit à de nouvelles façons innovantes d’investir sur les marchés africains. Daba, par exemple, permet aux investisseurs du monde entier d’acheter des actions d’entreprises africaines et d’ETFs sur la bourse régionale BRVM et fournit des ressources éducatives pour aider les investisseurs à comprendre les marchés africains.
Adopter l’Opportunité Africaine
À mesure que l’Afrique continue de se développer et que ses économies mûrissent, les ETFs offrent un moyen attrayant pour les investisseurs de participer à cette croissance.
Que vous choisissiez des ETFs de marché large pour une exposition continentale, des fonds spécifiques à un pays pour cibler des économies particulières ou que vous exploitiez de nouvelles plateformes numériques pour un accès plus granulaire, il existe de nombreuses options pour aligner votre stratégie d’investissement.
Points Clés sur l’Investissement dans les ETFs Africains
- Comprenez la diversité des économies africaines et les profils de risque variables
- Tenez compte de vos objectifs d’investissement et de votre tolérance au risque lors de la sélection des ETFs
- Explorez les plateformes traditionnelles et innovantes pour accéder aux ETFs africains
- Restez informé des développements économiques et politiques pouvant impacter les marchés africains
- Envisagez de consulter un conseiller financier pour vous assurer que les ETFs africains s’intègrent dans votre stratégie d’investissement globale
Comme pour tout investissement, une recherche approfondie et une réflexion minutieuse sont essentielles. Les ETFs africains peuvent offrir un potentiel de croissance excitant et des avantages de diversification, mais ils comportent également des risques uniques.
En adoptant une approche réfléchie et informée, les investisseurs peuvent potentiellement bénéficier du parcours économique de l’Afrique tout en construisant un portefeuille plus diversifié à l’échelle mondiale.
Pour ceux qui souhaitent investir dans des actions étrangères cotées à la BRVM en toute simplicité et avec des conseils d’experts, Daba offre une plateforme qui simplifie le processus, donnant accès à une large gamme d’actions, d’obligations, d’ETFs et de services d’investissement.
Vous pouvez télécharger l’application Daba Investment depuis le Play Store. Si vous êtes utilisateur d’iPhone, vous pouvez également télécharger l’application Daba Investment depuis l’App Store.