Africa offers immense investment potential to achieve sustainable development while generating financial returns.
As outlined in the 2022 UNDP Africa Investment Insights Report, data from 10 African countries shows over 150 investment opportunities across diverse sectors.
These present strong multiplier effects towards poverty reduction and shared prosperity on the continent.
Food and beverages, infrastructure, healthcare, education, and renewable energy emerged as the top five sectors for investment opportunities in the report.
Together, they accounted for over 60% of identified prospects spanning Eastern, Western, and Southern Africa.
The Daba Intelligence team further explores five more sectors. Read on to discover where Africa’s hottest investment opportunities lie.
Where To Invest In Africa: Here Are The Top 10 Most Promising Sectors
1. Food and Agriculture
The food and agriculture sector plays an integral economic role across Africa.
Despite the growth of its middle class and a reduced reliance on agriculture, Africa continues to experience a rising population and an increasing demand for food.
As a result, the continent offers substantial investment prospects in the agriculture and agribusiness sectors. These opportunities encompass investments in various aspects of the agricultural value chain, including farmland, agricultural inputs, processing, and agritech innovations.
Sub-Saharan Africa, in particular, faces significant agricultural needs that extend beyond fundamental elements like fertilizer, seeds, and irrigation to include essential infrastructure improvements.
Companies involved in enhancing roads, storage facilities, ports, and power grids in the region can also thrive as they support and facilitate the growth of Sub-Saharan Africa’s thriving agricultural operations.
These investments not only offer potential financial returns but also contribute to addressing the food security challenges that the region faces.

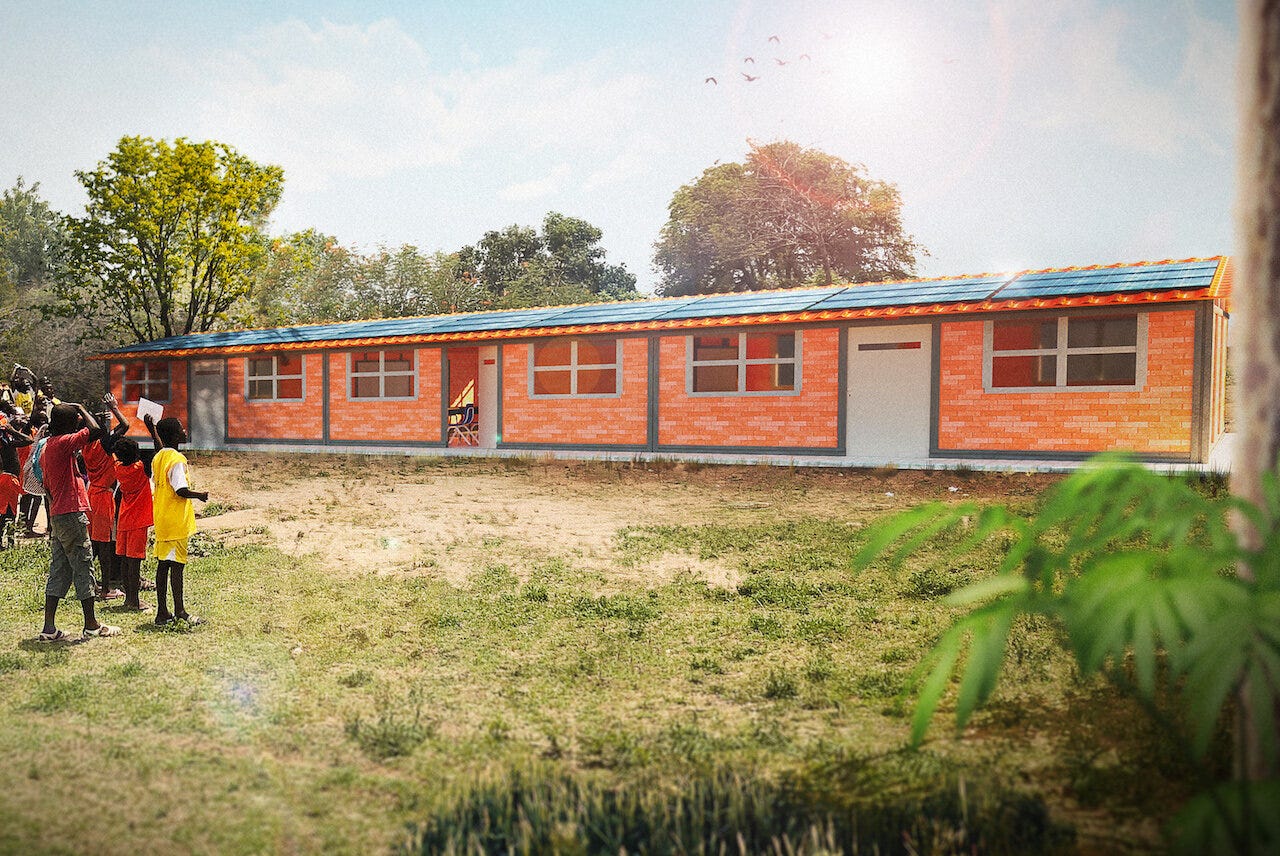
2. Infrastructure
Infrastructure needs remain critical for advancing socioeconomic outcomes. Requirements continue rising amidst rapid urbanization and industrialization.
While Africa’s infrastructure shortage is undeniable, it provides abundant investment opportunities – particularly for sectors like construction, telecommunications, energy, and transportation, to name a few.
The AfDB estimates that the continent needs up to $170 billion per year by 2025 to overhaul its infrastructure, with two-thirds of that being needed for entirely new infrastructure and the remaining one-third for maintenance.
Consequently, roads, housing, electricity, waste management, and other long-term projects signal strong public-private partnership potential.
3. Healthcare
The healthcare and prescription medicines sectors are estimated to have a combined worth of $3 billion, with innovator/patented medications contributing around $1.7 billion to this value. Over-the-counter medicines currently hold a value of $378 million.
Given the rise in pharmaceutical companies producing generic medicines, there’s a strong likelihood of increased investment in the nation’s healthcare sector.
This is particularly significant considering that 85% of Africa’s population depends on public health services.
It’s reasonable to anticipate that the public would readily embrace the National Health Insurance Plan, seeking access to more affordable medicines and treatment facilities.
Don’t miss out on exclusive investment opportunities in Africa! Download the Daba app today and unlock a world of potential returns while making a positive impact.
4. Education
Investing in education in Africa presents an opportunity to support the continent’s growth while yielding returns. Africa’s population is expected to double by 2050, driving demand for quality education.
Investment opportunities exist in building and running schools, educational technology, scholarships, and training programs. Private schools and higher education are particularly promising given the increasing demand for affordable, quality education.
Educational technology also provides a large-scale opportunity. With growing mobile and internet access, online platforms and apps can deliver affordable education in remote, underserved areas.

Providing African students and professionals with scholarships and training is another impactful investment. Partnerships with organizations already active in this space provide ideal investment channels.
Africa’s expanding youth population and demand for quality education create an opportunity to spur development through investment and generate financial returns.
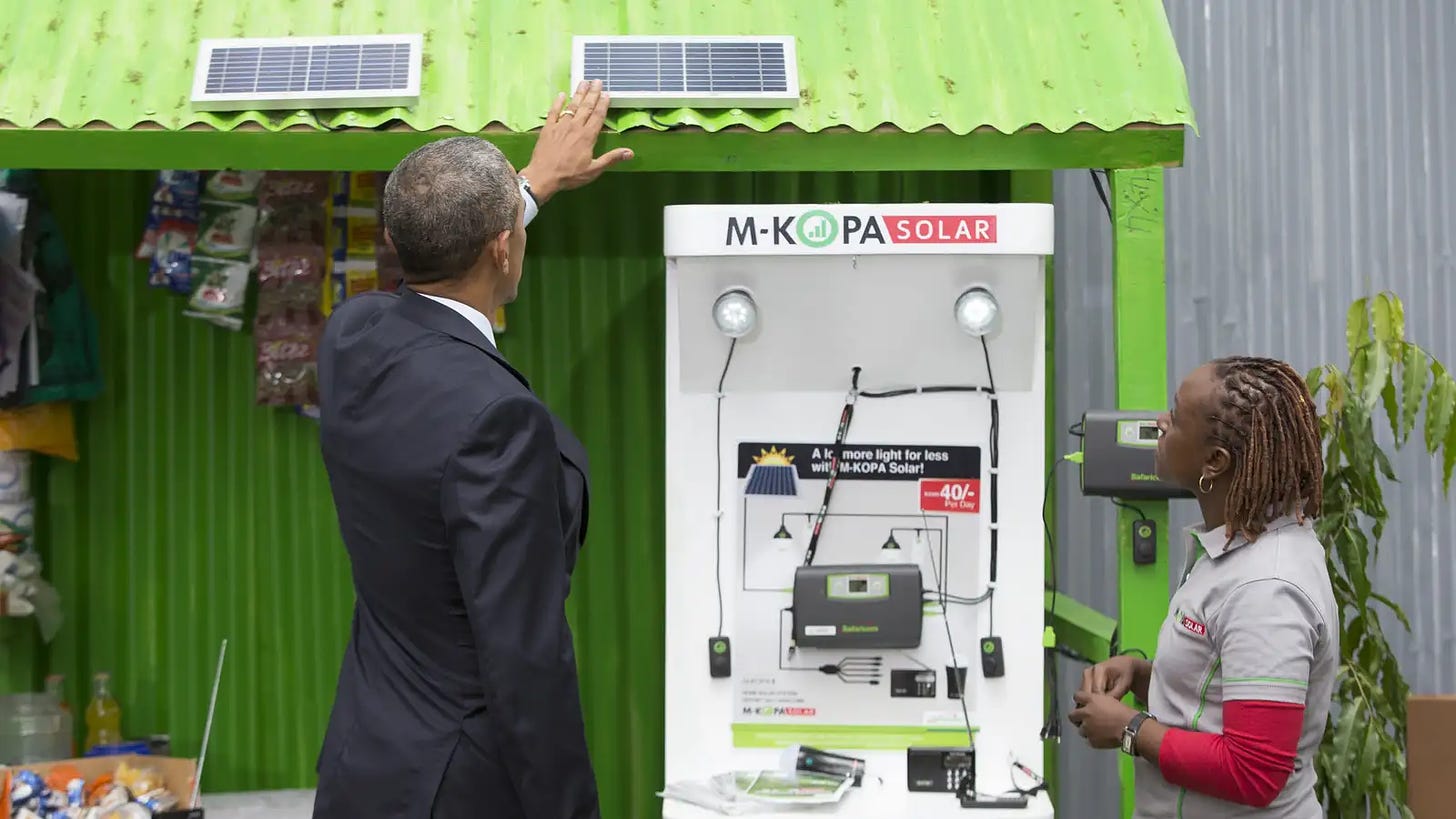
5. Renewable energy
Africa has abundant renewable energy resources that present major investment opportunities as the continent transitions to sustainable energy sources.
Solar and wind power are projected to see massive growth, with installed capacity increasing 100x for solar and 35x for wind by 2050. This will require billions in investment over the coming decades.
Morocco, South Africa, and North African countries will be key markets for solar and wind projects due to strong solar irradiation and wind resources, according to the World Economic Forum.
Hydroelectric power also offers substantial potential, with capacity expected to quadruple by 2050. Sub-Saharan African countries have the greatest remaining hydro resources to tap. Green hydrogen production is another area primed for major growth and exports, with projects already underway in Morocco, Namibia, and South Africa.
Cumulatively, nearly $3 trillion in capital expenditure on renewables and supporting infrastructure will be needed in Africa by 2050. Investing early can allow financial institutions to drive the transition and capitalize on long-term opportunities.

6. Commodity markets
Many African nations rely extensively on the trade of commodities. Some of them navigate the ups and downs of commodity cycles, exemplified by major oil-exporting countries like Angola and Nigeria, as well as copper-producing nations such as the Democratic Republic of Congo and Zambia.
According to UN estimates, Africa holds over 30% of global mineral reserves, including more than half the world’s reserves of gold, chrome, and platinum, a significant proportion of global diamond reserves, and 5% of naturally occurring lithium ore reserves.
The continent is also home to leading global exporters of agricultural commodities like cocoa (Cote d’Ivoire and Ghana), coffee (Ethiopia and Uganda), tea (Kenya), and cotton (Benin, Burkina Faso, Egypt, Sudan, and Mali).
Looking for a chance to make a difference while earning returns. Head over to our app to start investing in Africa’s growth today!
7. Retail and e-commerce
Africa’s expanding middle class, which has surged from 313 million people over the past 30 years, presents enticing investment prospects in retail-focused sectors.
For context, telecom companies in Africa have added over 400 million subscribers—more than the entire US population—since 2000.
The growth of Africa’s middle class can be attributed mainly to robust economic expansion, a shift towards salaried employment, and a move away from agriculture. The general pace may have been slower than expected but the continent’s demographic makeup remains attractive.
Catering to this market is a rapidly growing e-commerce industry, helped by an increasing number of Internet users. By 2025, Africa is forecast to have over half a billion online shoppers, with a 40% penetration, and a 17% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).

8. Real estate and housing
Urbanization and population growth in numerous African countries have fueled a rising demand for both residential and commercial real estate.
This dynamic landscape offers compelling opportunities in real estate development projects, allowing investors to capitalize on the continent’s growth momentum to potentially profit from the appreciating property values.
Many of the proven investment techniques that have succeeded in the Western world, such as long-term rentals, real estate investment trusts (REITs), vacation rentals, and lease options, can yield comparable returns in the African market.
Investors who prefer a cautious approach can consider options like REITs and other real estate funds. These investment vehicles can provide exposure to the real estate market while diversifying risk and potentially offering more stable returns.
9. Financial services and fintech
Africa’s financial services landscape has evolved over the last two decades and will play a critical role in securing the continent’s future.
Without sustainable funding and commercial credit, project development in key areas such as infrastructure, healthcare, and energy projects remain concepts rather than reality.
Regulatory reforms, the emergence of an urban middle class, and technological advancements allow financial institutions access to funding mechanisms to mitigate risk and maximize returns.
Want to take the next step in tapping Africa’s investment potential? Head over to our website or download the Daba app now to start your journey.

The emergence of fintech-driven solutions particularly holds great promise for this sector. Africa’s fintech potential was around $150 billion in 2020, per a report by McKinsey, fueled by insurance, retail, and SME lending.
Going forward, the market is projected to grow by 10% per year to reach around $230 billion by 2025, with the blockchain, payments, and wallets sectors expected to grow fastest.
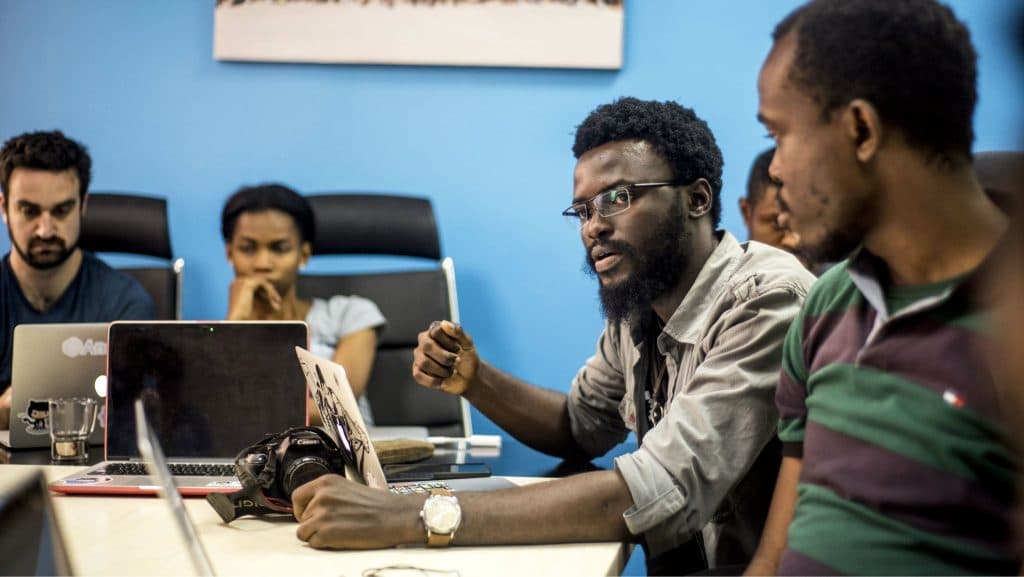
10. Technology and Innovation
Africa’s technology sector is experiencing rapid growth, with numerous innovative companies emerging to address real-world challenges and cater to consumer demands.
These African startups enjoy several advantages, including being early movers in the market and aligning with favorable demographic trends.
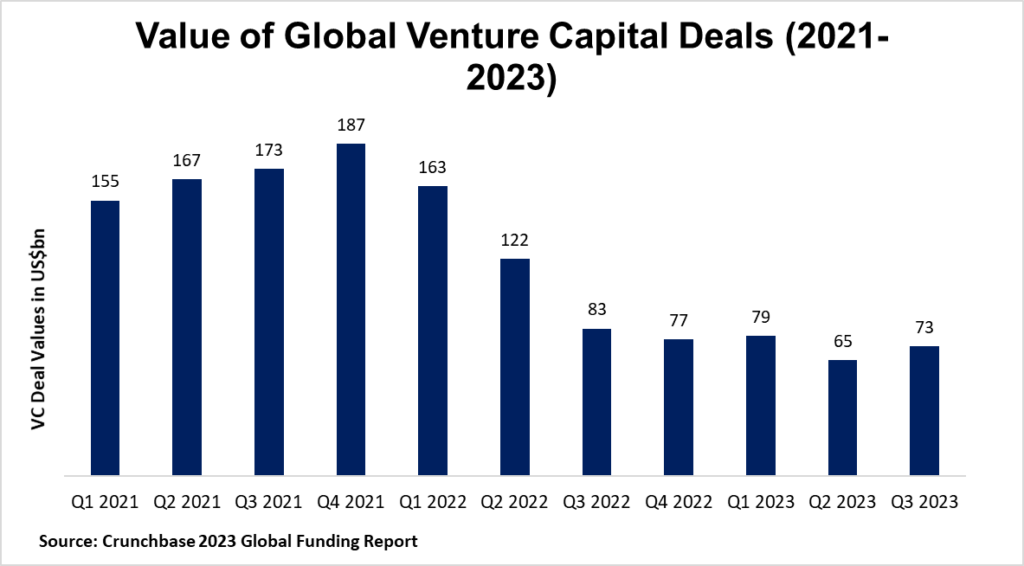
Despite the global economic slowdown experienced in 2022, African startups managed to secure record levels of funding from venture capitalists in the United States, Europe, and other regions.
Notably, the continent has even given rise to seven unicorns – startups valued at over $1 billion – further underlining the burgeoning potential and success of Africa’s tech industry.
Impact and Returns
Most opportunities are projected to generate a new positive outcome for underserved groups. This indicates they can meaningfully contribute to overcoming pressing sustainable development challenges.
They also offer attractive returns. About half forecast internal rates of return exceeding 20%, alongside high gross profit margins.
However, long investment horizons are common, especially in capital-intensive sectors like transportation and infrastructure where patience is key.

Financing and Implementation
Although some opportunities meet conditions for market-rate financing, most require blended public-private approaches.
These partnerships can address risks related to regulation, affordability, skills gaps, and enabling environment constraints.
Collaborations through regional bodies like the African Continental Free Trade Area also allow businesses to access larger markets, diversify portfolios, and share experiences. Additionally, they enable countries to focus interventions around their comparative advantages.
The Way Forward: Seize Africa’s Investment Opportunities Today
Africa provides abundant investment prospects to simultaneously deliver positive impact and financial gains over the medium to long term.
Institutional investors and development partners should continue working together to turn opportunities into reality in areas including agriculture, infrastructure, healthcare, education, and renewable energy.
And for retail investors, the good news is that the proliferation of investment platforms like Daba makes participating in investment opportunities in Africa’s emerging markets easier than ever.
For more content and analysis on economic trends and investment opportunities in Africa, get the Daba application today! And if you’re an institutional investor ready to explore opportunities tailored to your interests and objectives, fill out this interest form on the Daba website!